第5章 Newton-Cotes#
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
def trapezoidal(a, b, n, f):
h = (b-a)/n
x = np.linspace(a, b, num=n+1, endpoint=True)
s = 0.0
for i in range(n):
s = s + 0.5 * h *(f(x[i])+f(x[i+1]))
return s
def simpson(a, b, n, f):
h = (b-a)/n
x = np.linspace(a, b, num=n+1, endpoint=True)
s = 0.0
for i in range(n):
s = s + h / 6 *(f(x[i]) + 4*f(x[i]/2+x[i+1]/2) + f(x[i+1]))
return s
测试对\(\sin\)函数的积分#
f = lambda x : np.sin(x)
a = 0
b = np.pi
exact_value = 2
n_list = np.array(range(10, 105, 5))
err_list_trap = np.zeros(len(n_list))
err_list_simpson = np.zeros(len(n_list))
for n_idx in range(len(n_list)):
n = n_list[n_idx]
err_list_trap[n_idx] = np.abs(trapezoidal(a, b, n, f) - exact_value)
err_list_simpson[n_idx] = np.abs(simpson(a, b, n, f) - exact_value)
plt.figure(figsize=(4,3))
plt.plot(n_list, err_list_trap, 'o--', label="trapzoidal")
plt.plot(n_list, err_list_simpson, 'x-', label="simpson")
plt.legend(fontsize=14)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.xscale('log')
plt.xlabel('N',fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('Error',fontsize=14)
plt.tight_layout()
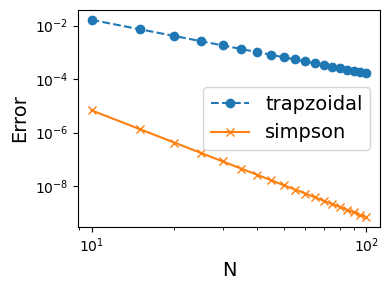
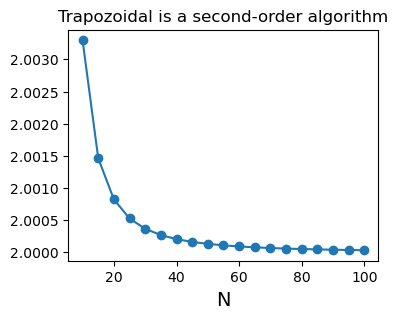
验证课本的对于复化梯形法的误差公式(4.2.15)#
plt.figure(figsize=(4,3))
plt.plot(n_list, err_list_trap / (((b-a)/n_list)**2/12), 'o-')
plt.title('Trapozoidal is a second-order algorithm')
plt.xlabel('N',fontsize=14)
plt.show()
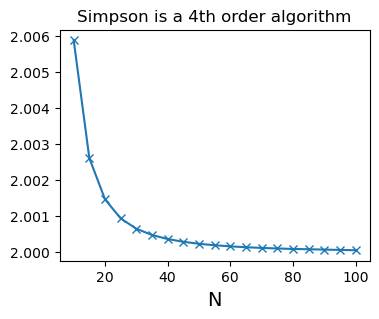
验证课本的对于复化Simpson的误差公式(4.2.16)#
plt.figure(figsize=(4,3))
plt.plot(n_list, err_list_simpson / ((((b-a)/n_list)**4) / 180 / 2**4), 'x-')
plt.title('Simpson is a 4th order algorithm')
plt.xlabel('N',fontsize=14)
plt.show()
Roomberg算法#
def Roomberg(a, b, n, f):
Ttable = np.zeros((n+1, n+1)) * np.nan
for k in range(n+1):
for m in range(k+1):
if m == 0:
Ttable[k,m] = trapezoidal(a, b, 2**k, f)
else:
alpha = 4**m
Ttable[k,m] = alpha/(alpha-1)*Ttable[k,m-1] - 1/(alpha-1)*Ttable[k-1,m-1]
return Ttable
f = lambda x : np.sin(x)
a = 0
b = np.pi
n = 6
Ttable = Roomberg(a, b, n, f)
pd.DataFrame(Ttable)
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.923671e-16 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1 | 1.570796e+00 | 2.094395 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 2 | 1.896119e+00 | 2.004560 | 1.998571 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 3 | 1.974232e+00 | 2.000269 | 1.999983 | 2.000006 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 4 | 1.993570e+00 | 2.000017 | 2.000000 | 2.000000 | 2.0 | NaN | NaN |
| 5 | 1.998393e+00 | 2.000001 | 2.000000 | 2.000000 | 2.0 | 2.0 | NaN |
| 6 | 1.999598e+00 | 2.000000 | 2.000000 | 2.000000 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
pd.DataFrame(np.abs(Ttable-2.0)).map(lambda x: f"{x:.2e}")
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.00e+00 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| 1 | 4.29e-01 | 9.44e-02 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| 2 | 1.04e-01 | 4.56e-03 | 1.43e-03 | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| 3 | 2.58e-02 | 2.69e-04 | 1.69e-05 | 5.55e-06 | nan | nan | nan |
| 4 | 6.43e-03 | 1.66e-05 | 2.48e-07 | 1.63e-08 | 5.41e-09 | nan | nan |
| 5 | 1.61e-03 | 1.03e-06 | 3.81e-09 | 5.97e-11 | 3.97e-12 | 1.32e-12 | nan |
| 6 | 4.02e-04 | 6.45e-08 | 5.93e-11 | 2.29e-13 | 4.00e-15 | 2.22e-16 | 6.66e-16 |
# 例子4.3的表格
def sinx_divide_x(x):
if x < 1.0e-5:
return 1
else:
return np.sin(x)/x
f = lambda x : sinx_divide_x(x)
a = 0
b = 1
n = 4
pd.DataFrame(Roomberg(a, b, n, f))
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.920735 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1 | 0.939793 | 0.946146 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 2 | 0.944514 | 0.946087 | 0.946083 | NaN | NaN |
| 3 | 0.945691 | 0.946083 | 0.946083 | 0.946083 | NaN |
| 4 | 0.945985 | 0.946083 | 0.946083 | 0.946083 | 0.946083 |